User:Tohline/SSC/Stability/BiPolytropes
Marginally Unstable Bipolytropes
Our aim is to determine whether or not there is a relationship between (1) equilibrium models at turning points along bipolytrope sequences and (2) bipolytropic models that are marginally (dynamically) unstable toward collapse (or dynamical expansion).

|
|---|
| | Tiled Menu | Tables of Content | Banner Video | Tohline Home Page | |
Overview
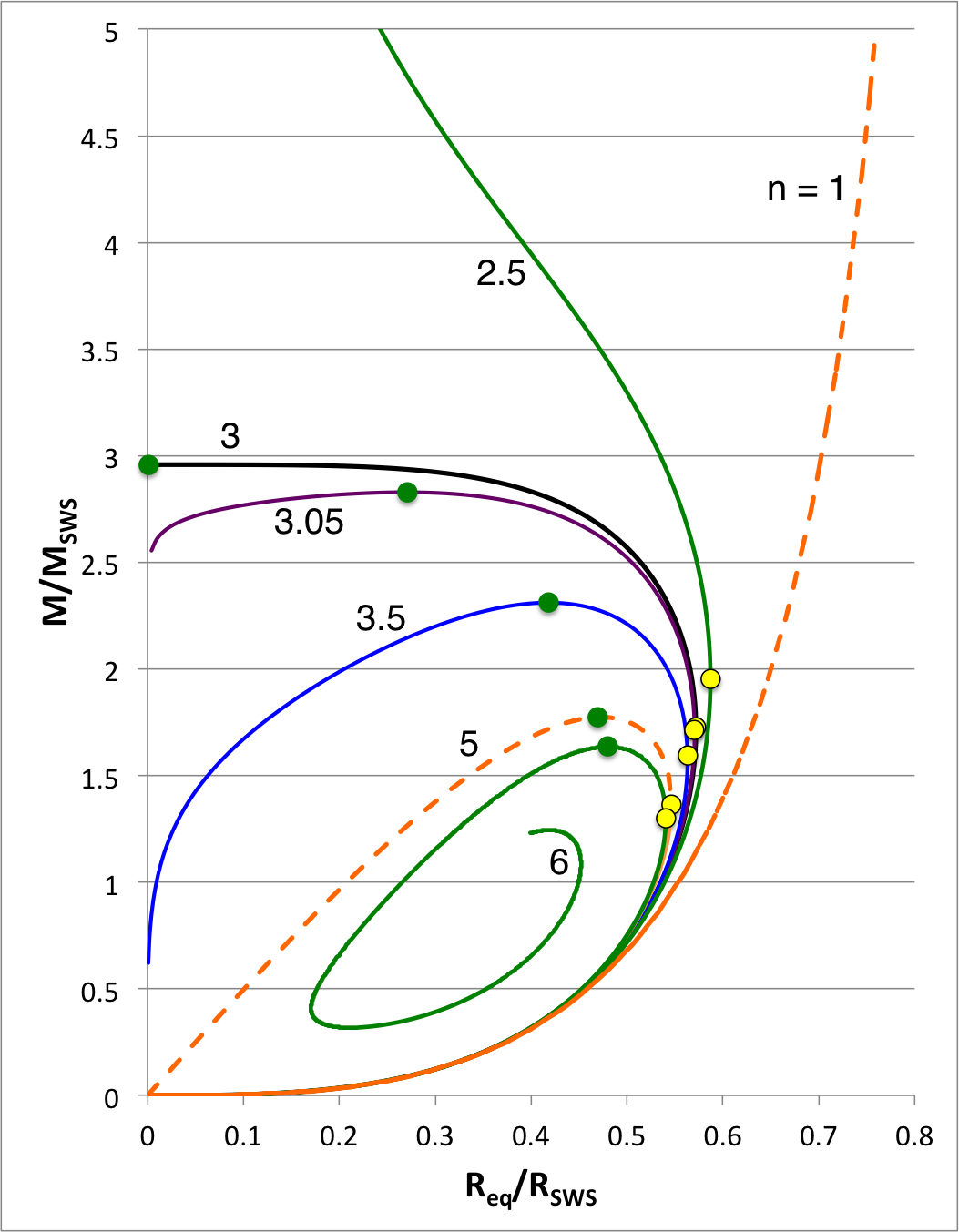
| Figure 1: Equilibrium Sequences of Pressure-Truncated Polytropes |
|---|
We expect the content of this chapter — which examines the relative stability of bipolytropes — to parallel in many ways the content of an accompanying chapter in which we have successfully analyzed the relative stability of pressure-truncated polytopes. Figure 1, shown here on the right, has been copied from a closely related discussion. The curves show the mass-radius relationship for pressure-truncated model sequences having a variety of polytropic indexes, as labeled, over the range <math>1 \le n \le 6</math>. (Another version of this figure includes the isothermal sequence.) On each sequence for which <math>~n \ge 3</math>, the green filled circle identifies the model with the largest mass. We have shown analytically that the oscillation frequency of the fundamental-mode of radial oscillation is precisely zero† for each one of these maximum-mass models. As a consequence, we know that each green circular marker identifies the point along its associated sequence that separates dynamically stable (larger radii) from dynamically unstable (smaller radii) models.
†In each case, the fundamental-mode oscillation frequency is precisely zero if, and only if, the adiabatic index governing expansions/contractions is related to the underlying structural polytropic index via the relation, <math>~\gamma_g = (n + 1)/n</math>, and if a constant surface-pressure boundary condition is imposed.
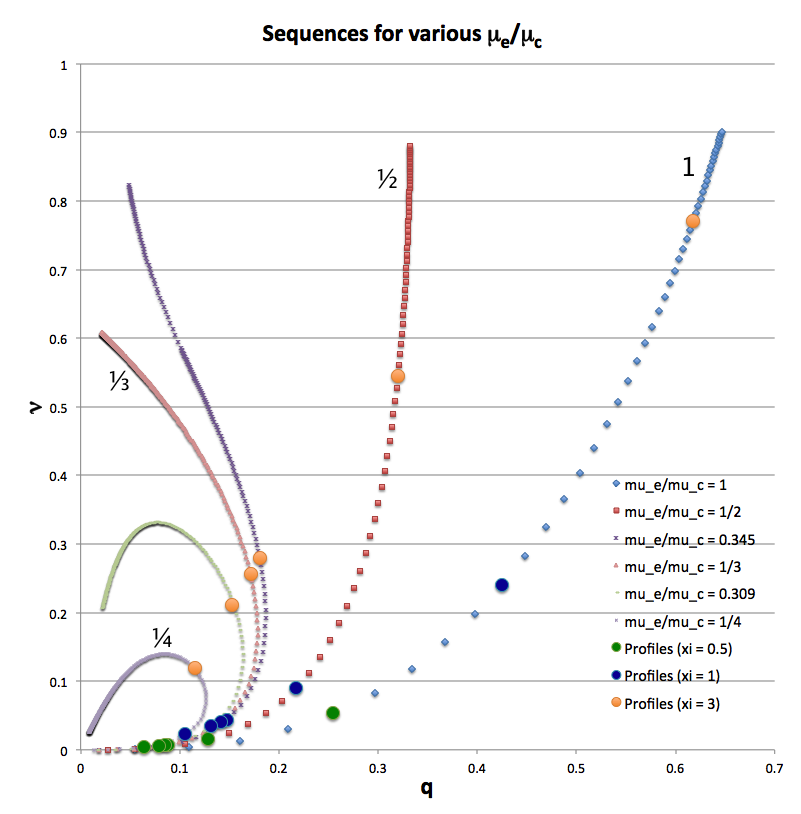
In another accompanying chapter, we have used purely analytic techniques to construct equilibrium sequences of spherically symmetric bipolytropes that have, <math>~(n_c,n_e) = (5,1)</math>. For a given choice of <math>~\mu_e/\mu_c</math> — the ratio of the mean-molecular weight of envelope material to the mean-molecular weight of material in the core — a physically relevant sequence of models can be constructed by steadily increasing the value of the dimensionless radius at the core/envelope interface, <math>~\xi_i</math>, from zero to infinity. Figure 2, which has been copied from this separate chapter, shows how the fractional core mass, <math>\nu \equiv M_\mathrm{core}/M_\mathrm{tot}</math>, varies with the fractional core radius, <math>q \equiv r_\mathrm{core}/R</math>, along sequences having six different values of <math>~\mu_e/\mu_c</math>: 1 (blue diamonds), ½ (red squares), 0.345 (dark purple crosses), ⅓ (pink triangles), 0.309 (light green dashes), and ¼ (purple asterisks). Along each of the model sequences, points marked by solid-colored circles correspond to models whose interface parameter, <math>~\xi_i</math>, has one of three values: 0.5 (green circles), 1 (dark blue circles), or 3 (orange circles).
When modeling bipolytropes, the default expectation is that an increase in <math>\xi_i</math> along a given sequence will correspond to an increase in the relative size — both the radius and the mass — of the core. As Figure 2 illustrates, this expectation is realized along the sequences marked by blue diamonds (<math>~\mu_e/\mu_c = 1</math>) and by red squares (<math>~\mu_e/\mu_c = </math>½). But the behavior is different along the other four illustrated sequences. For sufficiently large <math>~\xi_i</math>, the relative radius of the core begins to decrease. Furthermore, along sequences for which <math>~\mu_e/\mu_c < \tfrac{1}{3}</math>, eventually the fractional mass of the core reaches a maximum and, thereafter, decreases even as the value of <math>~\xi_i</math> continues to increase. (Additional properties of these equilibrium sequences are discussed in yet another accompanying chapter.)
The principal question is: Along bipolytropic sequences, are maximum-mass models associated with the onset of dynamical instabilities?
Planned Approach
| Figure 2: Equilibrium Sequences of Bipolytropes with <math>~(n_c,n_e) = (5,1)</math> | |
|---|---|
Ideally we would like to answer the just-stated "principal question" using purely analytic techniques. But, to date, we have been unable to fully address the relevant issues analytically, even in what would be expected to be the simplest case: bipolytropic models that have <math>~(n_c,n_e) = (0, 0)</math>. Instead, we will streamline the investigation a bit and proceed — at least initially — using a blend of techniques. We will investigate the relative stability of bipolytropic models having <math>~(n_c,n_e) = (5,1) </math> whose equilibrium structures are completely defined analytically; then the eigenvectors describing radial modes of oscillation will be determined, one at a time, by solving the relevant LAWE(s) numerically. We are optimistic that this can be successfully accomplished because we have had experience numerically integrating the LAWE that governs the oscillation of:
- Isolated n = 3 polytropes — including a quantitative comparison against Schwarzschild's (1941) published work;
- Pressure-truncated isothermal spheres — including a quantitative comparison against the published analysis of Taff & Van Horn (1974); and
- Pressure-truncated n = 5 polytropes.
A key reference throughout this investigation will be the paper by J. O. Murphy & R. Fiedler (1985b, Proc. Astr. Soc. of Australia, 6, 222). They studied Radial Pulsations and Vibrational Stability of a Sequence of Two Zone Polytropic Stellar Models. Specifically, their underlying equilibrium models were bipolytropes that have <math>~(n_c,n_e) = (1, 5)</math>. In an accompanying chapter, we describe in detail how Murphy & Fiedler obtained these equilibrium bipolytropic structures and detail some of their equilibrium properties.
Here are the steps we initially plan to take:
- Governing LAWEs:
- Identify the relevant LAWEs that govern the behavior of radial oscillations in the <math>~n_c = 5</math> core and, separately, in the <math>~n_e = 1</math> envelope. Check these LAWE specifications against the published work of Murphy & Fiedler (1985b).
- Determine the matching conditions that must be satisfied across the core/envelope interface. Be sure to take into account the critical interface jump conditions spelled out by P. Ledoux & Th. Walraven (1958), as we have already discussed in the context of an analysis of radial oscillations in zero-zero bipolytropes.
- Determine what surface boundary condition should be imposed on physically relevant LAWE solutions, i.e., on the physically relevant radial-oscillation eigenvectors.
- Initial Analysis:
- Choose a maximum-mass model along the bipolytropic sequence that has, for example, <math>~\mu_e/\mu_c = 1/4</math>. Hopefully, we will be able to identify precisely (analytically) where this maximum-mass model lies along the sequence. Yes! Our earlier analysis does provide an analytic prescription of the model that sits at the maximum-mass location along the chosen sequence.
- Solve the relevant eigenvalue problem for this specific model, initially for <math>~(\gamma_c, \gamma_e) = (6/5, 2)</math> and initially for the fundamental mode of oscillation.
Review of the Analysis by Murphy & Fiedler (1985b)
In the stability analysis presented by Murphy & Fiedler (1985b), the relevant polytropic indexes are, <math>~(n_c, n_e) = (1,5)</math>. Structural properties of the underlying equilibrium models have been reviewed in our accompanying discussion.
The Linear Adiabatic Wave Equation (LAWE) that is relevant to polytropic spheres may be written as,
|
<math>~0 = \frac{d^2x}{d\xi^2} + \biggl[ 4 - (n+1) Q \biggr] \frac{1}{\xi} \cdot \frac{dx}{d\xi} + (n+1) \biggl[ \biggl( \frac{\sigma_c^2}{6\gamma_g } \biggr) \frac{\xi^2}{\theta} - \alpha Q\biggr] \frac{x}{\xi^2} </math> |
|
|
where: <math>~Q(\xi) \equiv - \frac{d\ln\theta}{d\ln\xi} \, ,</math> <math>~\sigma_c^2 \equiv \frac{3\omega^2}{2\pi G\rho_c} \, ,</math> and, <math>~\alpha \equiv \biggl(3 - \frac{4}{\gamma_\mathrm{g}}\biggr)</math> |
|
|
See also …
|
As we have detailed separately, the boundary condition at the center of a polytropic configuration is,
<math>~\frac{dx}{d\xi} \biggr|_{\xi=0} = 0 \, ;</math>
and the boundary condition at the surface of an isolated polytropic configuration is,
|
<math>~\frac{d\ln x}{d\ln\xi}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~- \alpha + \frac{\omega^2}{\gamma_g } \biggl( \frac{1}{4\pi G \rho_c } \biggr) \frac{\xi}{(-\theta^')} </math> at <math>~\xi = \xi_s \, .</math> |
But this surface condition is not applicable to bipolytropes. Instead, let's return to the original, more general expression of the surface boundary condition:
|
<math>~ \frac{d\ln x}{d\ln\xi}\biggr|_s</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~- \alpha + \frac{\omega^2 R^3}{\gamma_g GM_\mathrm{tot}} \, .</math> |
|
Utilizing an accompanying discussion, let's examine the frequency normalization used by Murphy & Fiedler (1985b) (see the top of the right-hand column on p. 223):
Keep in mind, as well, that, in the notation we are using,
|
Let's apply these relations to the core and envelope, separately.
Envelope Layers With n = 5
The LAWE for n = 5 structures is, then,
|
<math>~0</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{d^2x}{d\eta^2} + \biggl[ 4 - 6Q_5 \biggr] \frac{1}{\eta} \cdot \frac{dx}{d\eta} + 6 \biggl[ \biggl( \frac{\sigma_c^2}{6\gamma_\mathrm{env} } \biggr) \frac{\eta^2}{\phi} - \alpha_\mathrm{env} Q_5\biggr] \frac{x}{\eta^2} </math> |
where,
|
<math>~Q_5</math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~- \frac{d\ln\phi}{d\ln\eta} \, .</math> |
From our accompanying discussion of the underlying equilibrium structure of <math>~(n_c, n_e) = (1, 5)</math> bipolytropes, we know that,
|
<math>~\phi</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\frac{B_0^{-1}\sin\Delta}{\eta^{1/2}(3-2\sin^2\Delta)^{1/2}} \, ,</math> |
and,
|
<math>~\frac{d\phi}{d\eta}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{B_0^{-1}[3\cos\Delta-3\sin\Delta + 2\sin^3\Delta] }{2\eta^{3/2}(3-2\sin^2\Delta)^{3/2}} \, . </math> |
where <math>~A_0</math> is a "homology factor," <math>~B_0</math> is an overall scaling coefficient, and we have introduced the notation,
<math>~\Delta \equiv \ln(A_0\eta)^{1/2} = \frac{1}{2} (\ln A_0 + \ln\eta) \, .</math>
Hence,
|
<math>~Q_5</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ - \eta \biggl[ \frac{\eta^{1/2}(3-2\sin^2\Delta)^{1/2}}{B_0^{-1}\sin\Delta} \biggr] \frac{B_0^{-1}[3\cos\Delta-3\sin\Delta + 2\sin^3\Delta] }{2\eta^{3/2}(3-2\sin^2\Delta)^{3/2}} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{ 3\sin\Delta - 3\cos\Delta - 2\sin^3\Delta }{2 \sin\Delta (3-2\sin^2\Delta)} \, . </math> |
And,
|
<math>~0</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{d^2x}{d\eta^2} ~+~ \biggl[ 4 + \frac{ 3(3\cos\Delta - 3\sin\Delta + 2\sin^3\Delta) }{ \sin\Delta (3-2\sin^2\Delta)} \biggr] \frac{1}{\eta} \cdot \frac{dx}{d\eta} ~+~ \biggl[ \biggl( \frac{\sigma_c^2}{\gamma_\mathrm{env} } \biggr) \frac{B_0 \eta^{1/2}(3-2\sin^2\Delta)^{1/2}}{\sin\Delta} ~+~ \frac{ 3\alpha_\mathrm{env} (3\cos\Delta -3\sin\Delta + 2\sin^3\Delta )}{\eta^2 \sin\Delta (3-2\sin^2\Delta)}\biggr] x </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{d^2x}{d\eta^2} ~+~ \biggl[ 4 ~+~ \frac{ 3(3\cos\Delta - \tfrac{3}{2}\sin\Delta - \tfrac{1}{2}\sin3\Delta) }{ \sin\Delta (2 + \cos2\Delta)} \biggr] \frac{1}{\eta} \cdot \frac{dx}{d\eta} ~+~ \biggl[\omega^2_k \theta_c \biggl( \frac{\gamma_g}{\gamma_\mathrm{env} } \biggr) \frac{B_0 \eta^{1/2}(2 + \cos2\Delta)^{1/2}}{\sin\Delta} ~+~ \frac{ 3\alpha_\mathrm{env} (3\cos\Delta -\tfrac{3}{2}\sin\Delta - \tfrac{1}{2}\sin3\Delta )}{\eta^2 \sin\Delta (2 + \cos2\Delta)}\biggr] x \, , </math> |
which matches the expression presented by Murphy & Fiedler (1985b) (see middle of the left column on p. 223 of their article) if we set <math>~\theta_c = 1</math> and <math>~\gamma_g/\gamma_\mathrm{env} = 1</math>.
Surface Boundary Condition
Next, pulling from our accompanying discussion of the stability of polytropes and an accompanying table that details the properties of <math>~(n_c, n_e) = (1, 5)</math> bipolytropes, the surface boundary condition is,
|
<math>~ \frac{d\ln x}{d\ln\eta}\biggr|_s</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~- \biggl(\frac{\gamma_g}{\gamma_\mathrm{env}}\biggr) \alpha + \frac{\omega^2 R^3}{\gamma_\mathrm{env} GM_\mathrm{tot}} </math> |
|
<math>~\Rightarrow ~~~ \frac{d\ln x}{d\ln\eta}\biggr|_s + \biggl(\frac{\gamma_g}{\gamma_\mathrm{env}}\biggr) \alpha </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{\omega^2 (R_s^*)^3}{\gamma_\mathrm{env} GM^*_\mathrm{tot}} \biggl( \frac{K_c}{G}\biggr)^{3 / 2}\biggl( \frac{K_c}{G}\biggr)^{-3 / 2} \frac{1}{\rho_0}</math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{\omega^2 }{\gamma_\mathrm{env} G\rho_0 } \biggl[ (2\pi)^{-1/2} \xi_i e^{2(\pi - \Delta_i)} \biggr]^3 \biggl[ \biggl( \frac{3}{2\pi} \biggr)^{1/2} \sin\xi_i \biggl( \frac{3}{\sin^2\Delta_i} - 2 \biggr)^{1/2} e^{(\pi - \Delta_i)} \biggr]^{-1} \biggl( \frac{\mu_e}{\mu_c}\biggr)</math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{\omega^2 }{\gamma_\mathrm{env}(2\pi G\rho_0)} \biggl( \frac{\mu_e}{\mu_c}\biggr) \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \biggl[ \frac{\xi_i^2}{\theta_i} \biggr] \biggl( \frac{3}{\sin^2\Delta_i} - 2 \biggr)^{-1 / 2} e^{5(\pi - \Delta_i)}</math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{\omega^2 }{\gamma_\mathrm{env}(2\pi G\rho_0)} \biggl( \frac{\mu_e}{\mu_c}\biggr) \frac{e^{5\pi}}{\sqrt{3}} \biggl[ \frac{\xi_i^2}{\theta_i} \biggr] \xi_i^{1 / 2}B\theta_i (\xi_i A)^{-5/2}</math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{\omega^2 }{\gamma_\mathrm{env}(2\pi G\rho_0)} \biggl( \frac{\mu_e}{\mu_c}\biggr) \frac{B e^{5\pi}}{\sqrt{3} ~A^{5 / 2}} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{2\omega_k^2 \theta_c}{(n_c+1)} \biggl( \frac{\mu_e}{\mu_c}\biggr) \frac{B e^{5\pi}}{\sqrt{3} ~A^{5 / 2}} \, . </math> |
Given that, <math>~\theta_c = 1</math> and <math>~n_c = 1</math>, his right-hand-side expression matches the equivalent term published by Murphy & Fiedler (1983b).
Core Layers With n = 1
And for n = 1 structures the LAWE is,
|
<math>~0</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{d^2x}{d\xi^2} + \biggl[ 4 - 2 Q_1 \biggr] \frac{1}{\xi} \cdot \frac{dx}{d\xi} + 2 \biggl[ \biggl( \frac{\sigma_c^2}{6\gamma_\mathrm{core} } \biggr) \frac{\xi^2}{\theta} - \alpha_\mathrm{core} Q_1\biggr] \frac{x}{\xi^2} </math> |
where,
|
<math>~Q_1</math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~- \frac{d\ln\theta}{d\ln\xi} \, .</math> |
Given that, for <math>~n = 1</math> polytropic structures,
<math> \theta(\xi) = \frac{\sin\xi}{\xi} </math> and <math> \frac{d\theta}{d\xi} = \biggl[ \frac{\cos\xi}{\xi}- \frac{\sin\xi}{\xi^2}\biggr] </math>
we have,
|
<math>~Q_1</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ - \frac{\xi^2}{\sin\xi} \biggl[ \frac{\cos\xi}{\xi}- \frac{\sin\xi}{\xi^2}\biggr] </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ 1 - \xi\cot\xi \, . </math> |
Hence, the governing LAWE for the core is,
|
<math>~0</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{d^2x}{d\xi^2} + \biggl[ 4 - 2 ( 1 - \xi\cot\xi ) \biggr] \frac{1}{\xi} \cdot \frac{dx}{d\xi} + 2 \biggl[ \biggl( \frac{\sigma_c^2}{6\gamma_\mathrm{core} } \biggr) \frac{\xi^3}{\sin\xi} - \alpha_\mathrm{core} ( 1 - \xi\cot\xi )\biggr] \frac{x}{\xi^2} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{d^2x}{d\xi^2} + \biggl[ 1 + \xi\cot\xi \biggr] \frac{2}{\xi} \cdot \frac{dx}{d\xi} + 2 \biggl[ \biggl( \frac{\sigma_c^2}{6\gamma_\mathrm{core} } \biggr) \frac{\xi^3}{\sin\xi} - \alpha_\mathrm{core} ( 1 - \xi\cot\xi )\biggr] \frac{x}{\xi^2} \, . </math> |
This can be rewritten as,
|
<math>~0</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{d^2x}{d\xi^2} + \frac{2}{\xi} \biggl[ 1 + \xi\cot\xi \biggr]\frac{dx}{d\xi} + \biggl[ \biggl( \frac{\sigma_c^2}{3\gamma_\mathrm{core} } \biggr) \frac{\xi}{\sin\xi} + \frac{2 \alpha_\mathrm{core} ( \xi\cos\xi - \sin\xi) }{\xi^2 \sin\xi} \biggr] x </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{d^2x}{d\xi^2} + \frac{2}{\xi} \biggl[ 1 + \xi\cot\xi \biggr]\frac{dx}{d\xi} + \biggl[ \frac{\gamma_g}{\gamma_\mathrm{core}}\biggl( \omega_k^2 \theta_c \biggr) \frac{\xi}{\sin\xi} + \frac{2 \alpha_\mathrm{core} ( \xi\cos\xi - \sin\xi) }{\xi^2 \sin\xi} \biggr] x \, , </math> |
which matches the expression presented by Murphy & Fiedler (1985b) (see middle of the left column on p. 223 of their article) if we set <math>~\theta_c = 1</math> and <math>~\gamma_g/\gamma_\mathrm{core} = 1</math>. This LAWE also appears in our separate discussion of radial oscillations in n = 1 polytropic spheres.
Interface Conditions
Here, we will simply copy the discussion already provided in the context of our attempt to analyze the stability of <math>~(n_c, n_e) = (0, 0)</math> bipolytropes; specifically, we will draw from STEP 4: in the Piecing Together subsection. Following the discussion in §§57 & 58 of P. Ledoux & Th. Walraven (1958), the proper treatment is to ensure that fractional perturbation in the gas pressure (see their equation 57.31),
|
<math>~\frac{\delta P}{P}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~- \gamma x \biggl( 3 + \frac{d\ln x}{d\ln \xi} \biggr) \, ,</math> |
is continuous across the interface. That is to say, at the interface <math>~(\xi = \xi_i)</math>, we need to enforce the relation,
|
<math>~0</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\biggl[ \gamma_c x_\mathrm{core} \biggl( 3 + \frac{d\ln x_\mathrm{core}}{d\ln \xi} \biggr) - \gamma_e x_\mathrm{env} \biggl( 3 + \frac{d\ln x_\mathrm{env}}{d\ln \xi} \biggr)\biggr]_{\xi=\xi_i}</math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\gamma_e \biggl[ \frac{\gamma_c}{\gamma_e} \biggl( 3 + \frac{d\ln x_\mathrm{core}}{d\ln \xi} \biggr) - \biggl( 3 + \frac{d\ln x_\mathrm{env}}{d\ln \xi} \biggr)\biggr]_{\xi=\xi_i}</math> |
|
<math>~\Rightarrow~~~ \frac{d\ln x_\mathrm{env}}{d\ln \xi} \biggr|_{\xi=\xi_i}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~3\biggl(\frac{\gamma_c}{\gamma_e} -1\biggr) + \frac{\gamma_c}{\gamma_e} \biggl( \frac{d\ln x_\mathrm{core}}{d\ln \xi} \biggr)_{\xi=\xi_i} \, .</math> |
In the context of this interface-matching constraint (see their equation 62.1), P. Ledoux & Th. Walraven (1958) state the following: In the static (i.e., unperturbed equilibrium) model … discontinuities in <math>~\rho</math> or in <math>~\gamma</math> might occur at some [radius]. In the first case — that is, a discontinuity only in density, while <math>~\gamma_e = \gamma_c</math> — the interface conditions imply the continuity of <math>~\tfrac{1}{x} \cdot \tfrac{dx}{d\xi}</math> at that [radius]. In the second case — that is, a discontinuity in the adiabatic exponent — the dynamical condition may be written as above. This implies a discontinuity of the first derivative at any discontinuity of <math>~\gamma</math>.
The algorithm that Murphy & Fiedler (1985b) used to "… [integrate] through each zone …" was designed "… with continuity in <math>~x</math> and <math>~dx/d\xi</math> being imposed at the interface …" Given that they set <math>~\gamma_c = \gamma_e = 5/3</math>, their interface matching condition is consistent with the one prescribed by P. Ledoux & Th. Walraven (1958).
Our Numerical Integration
Let's try to integrate this bipolytrope's LAWE from the center, outward, using as a guideline an accompanying Numerical Integration outline. Generally, for any polytropic index, the relevant LAWE can be written in the form,
|
<math>~\theta_i {x_i}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~- \biggl[\mathcal{A} \biggr] \frac{x_i'}{\xi_i} - \frac{(n+1)}{6} \biggl[ \mathcal{B} \biggr] x_i </math> |
where,
|
<math>~\mathcal{A}</math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~ 4\theta_i - (n+1)\xi_i (- \theta^')_i = \theta_i [ 4 - (n+1)Q_i] </math> |
|
<math>~\mathcal{B}</math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~ \frac{\sigma_c^2}{\gamma_g} - 2\alpha \biggl(- \frac{3\theta^'}{\xi} \biggr)_i = \mathfrak{F} + 2\alpha \biggl[ 1 - \biggl(- \frac{3\theta^'}{\xi} \biggr)_i \biggr] = \mathfrak{F} + 2\alpha \biggl[ 1 - \frac{3\theta_i}{\xi_i^2} \cdot Q_i \biggr] </math> |
|
<math>~ \mathfrak{F} </math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~ \biggl[ \frac{\sigma_c^2}{\gamma_g} - 2\alpha\biggr] = \biggl[ \frac{\sigma_c^2}{\gamma_g} - 2\biggl(3 - \frac{4}{\gamma_g} \biggr) \biggr] = \biggl[ \frac{(8 + \sigma_c^2)}{\gamma_g} - 6\biggr] </math> |
|
|
<math>~\Rightarrow~~~</math> |
<math>~ \sigma_c^2 = \gamma_g (\mathfrak{F} + 6) -8 \, . </math> |
This leads to a discrete, finite-difference representation of the form,
|
<math>~x_+ \biggl[2\theta_i + \frac{\delta\xi}{\xi_i} \cdot \mathcal{A}\biggr] </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ x_- \biggl[\frac{\delta\xi }{\xi_i} \cdot \mathcal{A} - 2\theta_i\biggr] + x_i\biggl\{4\theta_i - \frac{(\delta\xi)^2(n+1)}{3}\cdot \mathcal{B} \biggr\} \, .</math> |
This provides an approximate expression for <math>~x_+ \equiv x_{i+1}</math>, given the values of <math>~x_- \equiv x_{i-1}</math> and <math>~x_i</math>; this works for all zones, <math>~i = 3 \rightarrow N</math> as long as the center of the configuration is denoted by the grid index, <math>~i=1</math>. Note that,
|
<math>~\delta\xi</math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~\frac{\xi_\mathrm{max}}{(N - 1)} </math> |
and |
<math>~\xi_i</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~(i-1)\delta\xi \, . </math> |
In order to kick-start the integration, we will set the displacement function value to <math>~x_1 = 1</math> at the center of the configuration <math>~(\xi_1 = 0)</math>, then we will draw on the derived power-series expression to determine the value of the displacement function at the first radial grid line, <math>~\xi_2 = \delta\xi</math>, away from the center. Specifically, we will set,
|
<math>~ x_2 </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ x_1 \biggl[ 1 - \frac{(n+1) \mathfrak{F} (\delta\xi)^2}{60} \biggr] \, .</math> |
Integration Through the n = 1 Core
For an <math>~n = 1</math> core, we have,
<math> \theta_i = \frac{\sin\xi_i}{\xi_i} </math> and <math> Q_i = 1 - \xi_i \cot\xi_i \, . </math>
Hence,
|
<math>~\mathcal{A}_\mathrm{core}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{\sin\xi_i}{\xi_i} \biggl[ 4 - 2(1 - \xi_i \cot\xi_i) \biggr] = \frac{2\sin\xi_i}{\xi_i} \biggl[ 1 + \xi_i \cot\xi_i \biggr] </math> |
|
<math>~\mathcal{B}_\mathrm{core}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \mathfrak{F}_\mathrm{core} + 2\alpha_\mathrm{core} \biggl[ 1 - \frac{3\theta_i}{\xi_i^2} \cdot Q_i \biggr] = \mathfrak{F}_\mathrm{core} + 2\alpha_\mathrm{core} \biggl[ 1 - \frac{3\sin\xi_i}{\xi_i^3} \biggl( 1 - \xi_i \cot\xi_i \biggr)\biggr] \, . </math> |
So, first we choose a value of <math>~\sigma_c^2</math> and <math>~\gamma_c</math>, which means,
|
<math>~ \mathfrak{F}_\mathrm{core} </math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~ \biggl[ \frac{(8 + \sigma_c^2)}{\gamma_c} - 6\biggr] </math> |
Then, moving from the center of the configuration, outward to the interface at <math>~\xi_i = \xi_\mathrm{interface} ~~ \Rightarrow ~~\delta\xi = \xi_\mathrm{interface}/(N-1)</math>, we have,
|
<math>~x_1</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~1 \, ,</math> |
|
<math>~ x_2 </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ x_1 \biggl[ 1 - \frac{\mathfrak{F}_\mathrm{core} (\delta\xi)^2}{30} \biggr] \, ,</math> |
|
for <math>~i = 2 \rightarrow N \, ,</math> <math>~x_{i+1} \biggl[2\theta_i + \frac{\delta\xi}{\xi_i} \cdot \mathcal{A}_\mathrm{core} \biggr] </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ x_{i-1} \biggl[\frac{\delta\xi }{\xi_i} \cdot \mathcal{A}_\mathrm{core} - 2\theta_i\biggr] + x_i\biggl\{4\theta_i - \frac{(\delta\xi)^2(n+1)}{3}\cdot \mathcal{B}_\mathrm{core} \biggr\} \, .</math> |
At the interface — that is, when <math>~i=N</math> — the logarithmic slope of the displacement function is,
|
<math>~\frac{d\ln x}{d\ln\xi}\biggr|_\mathrm{interface}</math> |
<math>~\approx</math> |
<math>~ \frac{\xi_N}{x_N} \cdot \frac{(x_{N+1} - x_{N-1})}{2\delta\xi} \, . </math> |
Interface
Keep in mind that, as has been detailed in the accompanying equilibrium structure chapter, for <math>~(n_c, n_e) = (1, 5)</math> bipolytropes,
|
<math>~r^*</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\biggl( \frac{1}{2\pi}\biggr)^{1 / 2} \xi \, ,</math> |
for, |
<math>~0 \le \xi \le \xi_\mathrm{interface} \, .</math> |
|
<math>~r^*</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\biggl[ \biggl( \frac{\mu_e}{\mu_c}\biggr)^{-1} \biggl( \frac{3}{2\pi}\biggr)^{1 / 2} \biggr] \eta \, ,</math> |
for, |
<math>~\eta_\mathrm{interface} \le \eta \le \eta_s \, ;</math> |
|
<math>~\eta_s</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\biggl( \frac{\mu_e}{\mu_c}\biggr) \xi_s = \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\biggl( \frac{\mu_e}{\mu_c}\biggr) \biggl[ \xi e^{2(\pi - \Delta)} \biggr]_\mathrm{interface} \, . </math> |
|
|
We now need to determine what the slope is at the interface, viewed from the perspective of the envelope. From above, we deduce that,
|
<math>~\frac{d\ln y}{d\ln \eta} \biggr|_\mathrm{interface}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~3\biggl(\frac{\gamma_c}{\gamma_e} -1\biggr) + \frac{\gamma_c}{\gamma_e} \cdot \frac{d\ln x}{d\ln\xi}\biggr|_\mathrm{interface} \, .</math> |
Hence, letting the subscript "1" denote the interface location as viewed from the envelope, we have,
|
<math>~\frac{\eta_1}{y_1} \cdot \frac{(y_2 - y_0)}{ (\eta_2 - \eta_0)}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~3\biggl(\frac{\gamma_c}{\gamma_e} -1\biggr) + \frac{\gamma_c}{\gamma_e} \cdot \frac{d\ln x}{d\ln\xi}\biggr|_\mathrm{interface} \, .</math> |
|
<math>~\Rightarrow ~~~ y_0</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~y_2 - \frac{2 (\delta\eta) y_1}{\eta_1} \biggl\{ 3\biggl(\frac{\gamma_c}{\gamma_e} -1\biggr) + \frac{\gamma_c}{\gamma_e} \cdot \frac{d\ln x}{d\ln\xi}\biggr|_\mathrm{interface} \biggr\} \, .</math> |
Integration Through the n = 5 Envelope
For an <math>~n = 5</math> envelope, we have,
<math> \phi_i = \frac{B_0^{-1}\sin\Delta}{\eta^{1/2}(3-2\sin^2\Delta)^{1/2}} </math> and <math> Q_i = - \frac{d\ln\phi}{d\ln\eta} = \frac{ 3\sin\Delta - 3\cos\Delta - 2\sin^3\Delta }{2 \sin\Delta (3-2\sin^2\Delta)}\, , </math>
where <math>~A_0</math> is a "homology factor," <math>~B_0</math> is an overall scaling coefficient, and we have introduced the notation,
<math>~\Delta \equiv \ln(A_0\eta)^{1/2} = \frac{1}{2} (\ln A_0 + \ln\eta) \, .</math>
Hence,
|
<math>~\mathcal{A}_\mathrm{env}</math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~ \phi_i [ 4 - (n+1)Q_i] </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{B_0^{-1}\sin\Delta}{\eta^{1/2}(3-2\sin^2\Delta)^{1/2}}\biggl\{ 4 ~-~ 6 \biggl[ \frac{ 3\sin\Delta - 3\cos\Delta - 2\sin^3\Delta }{2 \sin\Delta (3-2\sin^2\Delta)} \biggr] \biggr\} </math> |
|
<math>~\mathcal{B}_\mathrm{env}</math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~ \frac{\sigma_c^2}{\gamma_e} - 2\alpha_\mathrm{env} \biggl(- \frac{3\phi^'}{\eta} \biggr)_i </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{1}{\gamma_e}\biggl[ \gamma_c (\mathfrak{F}_\mathrm{core} + 6) -8 \biggr] - 2\biggl[ 3 - \frac{4}{\gamma_e}\biggr] Q_i \biggl( \frac{3\phi_i }{\eta_i^2} \biggr) </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{\gamma_c}{\gamma_e}\biggl[ \mathfrak{F}_\mathrm{core} + 6 -\frac{8}{\gamma_c} \biggr] - 6\biggl[ 3 - \frac{4}{\gamma_e}\biggr] \frac{B_0^{-1}\sin\Delta}{\eta^{5/2}(3-2\sin^2\Delta)^{1/2}} \biggl[ \frac{ 3\sin\Delta - 3\cos\Delta - 2\sin^3\Delta }{2 \sin\Delta (3-2\sin^2\Delta)} \biggr] </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{\gamma_c}{\gamma_e}\biggl[ \mathfrak{F}_\mathrm{core} + 6 -\frac{8}{\gamma_c} \biggr] - 3B_0^{-1}\biggl[ 3 - \frac{4}{\gamma_e}\biggr] \biggl[ \frac{ 3\sin\Delta - 3\cos\Delta - 2\sin^3\Delta }{ \eta^{5/2}(3-2\sin^2\Delta)^{3 / 2}} \biggr] \, . </math> |
This leads to a discrete, finite-difference representation of the form,
|
<math>~y_+ \biggl[2\phi_i + \frac{\delta\eta}{\eta_i} \cdot \mathcal{A}_\mathrm{env} \biggr] </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ y_- \biggl[\frac{\delta\eta }{\eta_i} \cdot \mathcal{A}_\mathrm{env} - 2\phi_i\biggr] + y_i\biggl[4\phi_i - 2(\delta\eta)^2 \cdot \mathcal{B}_\mathrm{env} \biggr] </math> |
This provides an approximate expression for <math>~y_+ \equiv y_{i+1}</math>, given the values of <math>~y_- \equiv y_{i-1}</math> and <math>~y_i</math>; this works for all zones, <math>~i = 3 \rightarrow M</math> as long as the interface between the core and the envelope of the configuration is denoted by the grid index, <math>~i=1</math>. Note that,
|
<math>~\delta\eta</math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~\frac{\eta_\mathrm{surf}- \eta_\mathrm{interface} }{M - 1} </math> |
and |
<math>~\eta_i</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\eta_\mathrm{interface} + (i-1)\delta\eta \, . </math> |
At the interface, we need special treatment in order to ensure that both the amplitude and the first derivative of the displacement function behave properly. Specifically, when <math>~i = 1</math>, we must set, <math>~y_1 = x_N</math> and <math>~\eta_1 = (\mu_e/\mu_c)\xi_N/\sqrt{3}</math>. Then the value of <math>~y_2</math> is obtained from the expression,
|
<math>~y_2 \biggl[2\phi_1 + \frac{\delta\eta}{\eta_1} \cdot \mathcal{A}_\mathrm{env} \biggr] </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ y_0 \biggl[\frac{\delta\eta }{\eta_1} \cdot \mathcal{A}_\mathrm{env} - 2\phi_1\biggr] + y_1\biggl\{4\phi_1 - 2(\delta\eta)^2 \cdot \mathcal{B}_\mathrm{env} \biggr\} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ y_1\biggl[ 4\phi_1 - 2(\delta\eta)^2 \cdot \mathcal{B}_\mathrm{env} \biggr] + \biggl[\frac{\delta\eta }{\eta_1} \cdot \mathcal{A}_\mathrm{env} - 2\phi_1\biggr] \biggl\{ y_2 ~-~ \frac{2 (\delta\eta) y_1}{\eta_1} \biggl[ 3\biggl(\frac{\gamma_c}{\gamma_e} -1\biggr) + \frac{\gamma_c}{\gamma_e} \cdot \frac{d\ln x}{d\ln\xi}\biggr|_\mathrm{interface} \biggr] \biggr\} </math> |
|
<math>~\Rightarrow~~~y_2 \biggl[4\phi_1 \biggr] </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ y_1\biggl[ 4\phi_1 - 2(\delta\eta)^2 \cdot \mathcal{B}_\mathrm{env} \biggr] ~-~ \frac{2 (\delta\eta) y_1}{\eta_1} \biggl[\frac{\delta\eta }{\eta_1} \cdot \mathcal{A}_\mathrm{env} - 2\phi_1\biggr] \biggl\{3\biggl(\frac{\gamma_c}{\gamma_e} -1\biggr) + \frac{\gamma_c}{\gamma_e} \cdot \frac{d\ln x}{d\ln\xi}\biggr|_\mathrm{interface} \biggr\} \, . </math> |
Begin Our Analysis
Relevant LAWEs
The LAWE that is relevant to polytropic spheres may be written as,
|
<math>~0 = \frac{d^2x}{d\xi^2} + \biggl[ 4 - (n+1) Q \biggr] \frac{1}{\xi} \cdot \frac{dx}{d\xi} + (n+1) \biggl[ \biggl( \frac{\sigma_c^2}{6\gamma_g } \biggr) \frac{\xi^2}{\theta} - \alpha Q\biggr] \frac{x}{\xi^2} </math> |
|
|
where: <math>~Q(\xi) \equiv - \frac{d\ln\theta}{d\ln\xi} \, ,</math> <math>~\sigma_c^2 \equiv \frac{3\omega^2}{2\pi G\rho_c} \, ,</math> and, <math>~\alpha \equiv \biggl(3 - \frac{4}{\gamma_\mathrm{g}}\biggr)</math> |
|
Core Layers With n = 5
The LAWE for n = 5 structures is,
|
<math>~0</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{d^2x}{d\xi^2} + \biggl[ 4 - 6Q_5 \biggr] \frac{1}{\xi} \cdot \frac{dx}{d\xi} + 6 \biggl[ \biggl( \frac{\sigma_c^2}{6\gamma_\mathrm{core} } \biggr) \frac{\xi^2}{\theta_5} - \alpha_\mathrm{core} Q_5\biggr] \frac{x}{\xi^2} </math> |
where,
|
<math>~Q_5</math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~- \frac{d\ln\theta_5}{d\ln\xi} \, .</math> |
From our study of the equilibrium structure of <math>~(n_c, n_e) = (5, 1)</math> bipolytropes, we have,
|
<math>~ \theta_5 </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\biggl[ 1 + \frac{1}{3}\xi^2 \biggr]^{-1 / 2} \, ;</math> |
|
<math>~ \frac{d\theta_5}{d\xi} </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~- \frac{\xi}{3}\biggl[ 1 + \frac{1}{3}\xi^2 \biggr]^{-3/2} \, .</math> |
|
<math>~\Rightarrow~~~ Q_5 = - \frac{\xi}{\theta_5} \cdot \frac{d\theta_5}{d\xi} </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \biggl[ 1 + \frac{1}{3}\xi^2 \biggr]^{1 / 2} \frac{\xi^2}{3}\biggl[ 1 + \frac{1}{3}\xi^2 \biggr]^{-3 / 2} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{\xi^2}{3}\biggl[ 1 + \frac{1}{3}\xi^2 \biggr]^{-1} \, . </math> |
Hence, for the core the governing LAWE is,
|
<math>~0</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{d^2x}{d\xi^2} + \biggl\{ 4 - 2\xi^2\biggl[ 1 + \frac{1}{3}\xi^2 \biggr]^{-1} \biggr\} \frac{1}{\xi} \cdot \frac{dx}{d\xi} + 6 \biggl\{ \biggl( \frac{\sigma_c^2}{6\gamma_\mathrm{core} } \biggr) \xi^2\biggl[ 1 + \frac{1}{3}\xi^2 \biggr]^{1 / 2} - ~\alpha_\mathrm{core} \cdot \frac{\xi^2}{3}\biggl[ 1 + \frac{1}{3}\xi^2 \biggr]^{-1} \biggr\} \frac{x}{\xi^2} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{d^2x}{d\xi^2} + \biggl\{ 2 - \xi^2\biggl[ 1 + \frac{1}{3}\xi^2 \biggr]^{-1} \biggr\} \frac{2}{\xi} \cdot \frac{dx}{d\xi} + \biggl\{ \biggl( \frac{\sigma_c^2}{\gamma_\mathrm{core} } \biggr) \biggl[ 1 + \frac{1}{3}\xi^2 \biggr]^{1 / 2} - ~2\alpha_\mathrm{core} \biggl[ 1 + \frac{1}{3}\xi^2 \biggr]^{-1} \biggr\} x </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{d^2x}{d\xi^2} + \biggl\{ 2 - 3\xi^2\biggl[ 3 + \xi^2 \biggr]^{-1} \biggr\} \frac{2}{\xi} \cdot \frac{dx}{d\xi} + \biggl\{ \biggl( \frac{\sigma_c^2}{\sqrt{3}~\gamma_\mathrm{core} } \biggr) \biggl[ 3 + \xi^2 \biggr]^{1 / 2} - ~6\alpha_\mathrm{core} \biggl[ 3 + \xi^2 \biggr]^{-1} \biggr\} x </math> |
|
<math>~\Rightarrow ~~~ 0</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ (3 + \xi^2) \frac{d^2x}{d\xi^2} + \biggl\{ 2(3 + \xi^2) - 3\xi^2 \biggr\} \frac{2}{\xi} \cdot \frac{dx}{d\xi} + \biggl\{ \biggl( \frac{\sigma_c^2}{\sqrt{3}~\gamma_\mathrm{core} } \biggr) ( 3 + \xi^2 )^{3 / 2} - ~6\alpha_\mathrm{core} \biggr\} x </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ (3 + \xi^2) \frac{d^2x}{d\xi^2} + ( 6 - \xi^2 ) \frac{2}{\xi} \cdot \frac{dx}{d\xi} + \biggl[ \biggl( \frac{\sigma_c^2}{\sqrt{3}~\gamma_\mathrm{core} } \biggr) ( 3 + \xi^2 )^{3 / 2} - ~6\alpha_\mathrm{core} \biggr] x \, . </math> |
This exactly matches our derivation performed in the context of pressure-truncated polytropes. When we insert the eigenfunction obtained via a Eureka Moment on 3/6/2017,
|
<math>~x</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~x_0\biggl[1 - \frac{\xi^2}{15}\biggr] \, ,</math> |
|
<math>~\Rightarrow~~~ \frac{dx}{d\xi}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~- \frac{2x_0 \xi}{15} </math> |
|
<math>~\Rightarrow~~~ \frac{d^2x}{d\xi^2}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~- \frac{2x_0 }{15} \, ,</math> |
we obtain,
|
<math>~ (3 + \xi^2) \frac{d^2x}{d\xi^2} + ( 6 - \xi^2 ) \frac{2}{\xi} \cdot \frac{dx}{d\xi} + \biggl[ \biggl( \frac{\sigma_c^2}{\sqrt{3}~\gamma_\mathrm{core} } \biggr) ( 3 + \xi^2 )^{3 / 2} - ~6\alpha_\mathrm{core} \biggr] x </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ -~(3 + \xi^2) \frac{2x_0 }{15} - 2( 6 - \xi^2 ) \frac{2x_0 }{15} + \frac{x_0}{15}\biggl[ \biggl( \frac{\sigma_c^2}{\sqrt{3}~\gamma_\mathrm{core} } \biggr) ( 3 + \xi^2 )^{3 / 2} - ~6\alpha_\mathrm{core} \biggr] (15 - \xi^2) </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ -\frac{x_0}{15} \biggl\{ 2(3 + \xi^2) + 4( 6 - \xi^2 ) - \biggl[ \biggl( \frac{\sigma_c^2}{\sqrt{3}~\gamma_\mathrm{core} } \biggr) ( 3 + \xi^2 )^{3 / 2} - ~6\alpha_\mathrm{core} \biggr] (15 - \xi^2) \biggr\} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ -\frac{x_0}{15} \biggl\{ 30 - 2\xi^2 ~+ ~6\alpha_\mathrm{core} (15 - \xi^2) ~- \biggl[ \biggl( \frac{\sigma_c^2}{\sqrt{3}~\gamma_\mathrm{core} } \biggr) ( 3 + \xi^2 )^{3 / 2} \biggr] (15 - \xi^2) \biggr\} \, . </math> |
The right-hand-side goes to zero if <math>~\alpha_\mathrm{core} = - 1/3</math> and <math>~\sigma_c = 0</math>. Also, notice that,
|
<math>~ \frac{d\ln x}{d\ln \xi}\biggr|_\mathrm{core} = \frac{\xi}{x}\cdot \frac{dx}{d\xi} \biggr|_\mathrm{core}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~- \frac{2x_0 \xi^2}{15} \biggl\{ x_0\biggl[1 - \frac{\xi^2}{15}\biggr] \biggr\}^{-1}</math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~- \biggl\{ \frac{15}{2\xi^2}\biggl[\frac{15 -\xi^2}{15}\biggr] \biggr\}^{-1}</math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~- \biggl[\frac{15 -\xi^2}{2\xi^2}\biggr]^{-1}</math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~2 \biggl[1 - \frac{15}{\xi^2} \biggr]^{-1} \, .</math> |
So, with <math>~\gamma_c = 6/5</math> and <math>~\gamma_e = 2</math> we need,
|
<math>~\frac{d\ln x_\mathrm{env}}{d\ln \xi} \biggr|_{\xi=\xi_i}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~3\biggl(\frac{\gamma_c}{\gamma_e} -1\biggr) + \frac{\gamma_c}{\gamma_e} \biggl( \frac{d\ln x_\mathrm{core}}{d\ln \xi} \biggr)_{\xi=\xi_i} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~3\biggl(\frac{3}{5} -1\biggr) + \frac{6}{5} \biggl[1 - \frac{15}{\xi_i^2} \biggr]^{-1} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\frac{6}{5} \biggl\{ \biggl[\frac{\xi_i^2 - 15}{\xi_i^2} \biggr]^{-1} - 1 \biggr\} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\frac{6}{5} \biggl[\frac{15}{\xi_i^2 - 15} \biggr] \, .</math> |
Envelope Layers With n = 1
And for n = 1 structures the LAWE is,
|
<math>~0</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{d^2x}{d\eta^2} + \biggl[ 4 - 2 Q_1 \biggr] \frac{1}{\eta} \cdot \frac{dx}{d\eta} + 2 \biggl[ \biggl( \frac{\sigma_c^2}{6\gamma_\mathrm{env} } \biggr) \frac{\eta^2}{\theta_1} - \alpha_\mathrm{env} Q_1\biggr] \frac{x}{\eta^2} </math> |
where,
|
<math>~Q_1</math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~- \frac{d\ln\theta_1}{d\ln\eta} \, .</math> |
As has already been pointed out, above, for n = 1 polytropic spheres, this LAWE becomes,
|
<math>~0</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{d^2x}{d\eta^2} + \frac{2}{\eta} \biggl[ 1 + \eta\cot\eta \biggr]\frac{dx}{d\eta} + \biggl[ \frac{\gamma_g}{\gamma_\mathrm{env}}\biggl( \omega_k^2 \theta_c \biggr) \frac{\eta}{\sin\eta} + \frac{2 \alpha_\mathrm{env} ( \eta\cos\eta - \sin\eta) }{\eta^2 \sin\eta} \biggr] x \, . </math> |
In a separate chapter, we explain that the analytically defined eigenfunction that satisfies this LAWE — when <math>~\omega_k^2 = 0</math> and <math>~\alpha_\mathrm{env} = +1</math> — is,
|
<math>~x_P\biggr|_{n=1}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{3b_e}{\eta^2}\biggl[ 1- \eta \cot\eta \biggr] \, . </math> |
Summary
For a given choice of the equilibrium model parameters, <math>~\xi_i</math> and <math>~\mu_e/\mu_c</math>, we can pull the parameters and profiles of the base equilibrium model from our accompanying chapter on <math>~(n_c, n_e) = (5, 1)</math> bipolytropes. Note, in particular, that:
|
<math>~r^*</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\biggl( \frac{3}{2\pi}\biggr)^{1 / 2} \xi \, ,</math> |
for, |
<math>~0 \le \xi \le \xi_i \, .</math> |
|
<math>~r^*</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\biggl[ \biggl( \frac{\mu_e}{\mu_c}\biggr)^{-1} \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}} \biggl(1 + \frac{\xi_i^2}{3} \biggr) \biggr] \eta \, ,</math> |
for, |
<math>~\eta_i \le \eta \le \eta_s \, ;</math> |
|
<math>~\eta_s</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \eta_i + \frac{\pi}{2} + \tan^{-1} \biggl[\frac{1}{\eta_i} - \frac{\xi_i}{\sqrt{3}} \biggr] \, . </math> |
|
|
Then, for a choice of the pair of exponents, <math>~\gamma_\mathrm{core}</math> and <math>~\gamma_\mathrm{env}</math>, that govern the behavior of adiabatic oscillations, the LAWE to be numerically integrated is:
|
<math>~0</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ (3 + \xi^2) \frac{d^2x_\mathrm{core}}{d\xi^2} + ( 6 - \xi^2 ) \frac{2}{\xi} \cdot \frac{dx_\mathrm{core}}{d\xi} + \biggl[ \biggl( \frac{\sigma_c^2}{\sqrt{3}~\gamma_\mathrm{core} } \biggr) ( 3 + \xi^2 )^{3 / 2} - ~6\alpha_\mathrm{core} \biggr] x_\mathrm{core} \, , </math> |
for, |
<math>~0 \le \xi \le \xi_i \, ;</math> |
|
<math>~0</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{d^2x_\mathrm{env}}{d\eta^2} + \biggl[ 1 + \eta\cot\eta \biggr] \frac{2}{\eta} \cdot \frac{dx_\mathrm{env}}{d\eta} + 2 \biggl[ \biggl( \frac{\sigma_c^2}{6\gamma_\mathrm{env} } \biggr) \frac{\eta^3}{\sin\eta} - \alpha_\mathrm{env} ( 1 - \eta\cot\eta )\biggr] \frac{x_\mathrm{env}}{\eta^2} \, , </math> |
for, |
<math>~\eta_i \le \eta \le \eta_s \, .</math> |
The boundary conditions at the center of the configuration are, <math>~x_\mathrm{env} = 1</math>, while <math>~dx_\mathrm{env}/d\xi = 0</math>.
As described above, the two interface boundary conditions are, <math>~x_\mathrm{env} = x_\mathrm{core}</math>, and,
|
<math>~\frac{d\ln x_\mathrm{env}}{d\ln \xi} \biggr|_{\xi=\xi_i}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~3\biggl(\frac{\gamma_\mathrm{core}}{\gamma_\mathrm{env}} -1\biggr) + \frac{\gamma_\mathrm{core}}{\gamma_\mathrm{env}} \biggl( \frac{d\ln x_\mathrm{core}}{d\ln \xi} \biggr)_{\xi=\xi_i} \, .</math> |
Finally, drawing from a related discussion of the surface boundary condition for isolated n = 3 polytropes, at the surface we need,
|
<math>~\frac{d\ln x_\mathrm{env}}{d\ln \eta}\biggr|_\mathrm{surface}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\frac{1}{\gamma_\mathrm{env}} \biggl( 4 - 3\gamma_\mathrm{env} + \frac{\omega^2 R^3}{GM_\mathrm{tot}}\biggr) </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\biggl[ \frac{3\omega^2 R^3}{4\pi G \gamma_\mathrm{env} \bar\rho} - \alpha_\mathrm{env} \biggr] </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\frac{1}{2} \biggl[ \frac{\sigma_c^2}{\gamma_\mathrm{env} } \biggl(\frac{\rho_c}{\bar\rho}\biggr) -2 \alpha_\mathrm{env} \biggr] \, ,</math> |
where, for an <math>~(n_c, n_e) = (5, 1)</math> bipolytrope,
|
<math>~\frac{\rho_c}{\bar\rho}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \biggl(\frac{\mu_e}{\mu_c}\biggr)^{-1} \frac{\eta_s^2}{3A\theta_i^5} \, . </math> |
See Also
- K. De et al. (12 October 2018, Science, Vol. 362, No. 6411, pp. 201 - 206), A Hot and Fast Ultra-stripped Supernova that likely formed a Compact Neutron Star Binary.

|
|---|
|
© 2014 - 2021 by Joel E. Tohline |