CGH: Appertures that are Parallel to the Image Screen
This chapter is intended primarily to replicate §I.A from the online class notes — see also an associated Preface and the original Table of Contents — that I developed in conjunction with a course that I taught in 1999 on the topic of Computer Generated Holography (CGH) for a subset of LSU physics majors who were interested in computational science.
One-Dimensional Aperture
General Concept
Consider the amplitude (and phase) of light that is incident at a location <math>~y_1</math> on an image screen that is located a distance <math>~Z</math> from a slit of width <math>~w</math>. First, as illustrated in Figure 1, consider the contribution due only to two rays of light: one coming from location <math>~Y_1</math> at the top edge of the slit (a distance <math>~D_1</math> from point <math>~y_1</math> on the screen) and another coming from location <math>~Y_2</math> at the bottom edge of the slit (a distance <math>~D_2</math> from the same point on the screen).
| Figure 1 |
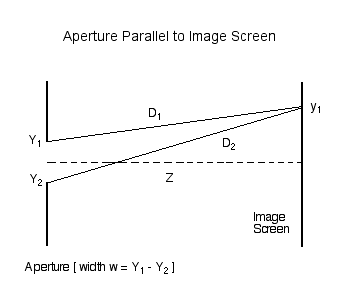 |
See Also
- Tohline, J. E., (2008) Computing in Science & Engineering, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 84-85 — Where is My Digital Holographic Display? [ PDF ]


