Difference between revisions of "User:Tohline/Appendix/CGH/ParallelApertures"
(Created page with '<!-- __FORCETOC__ will force the creation of a Table of Contents --> <!-- __NOTOC__ will force TOC off --> =CGH: Appertures that are Parallel to the Image Screen= This chapter i…') |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<!-- __NOTOC__ will force TOC off --> | <!-- __NOTOC__ will force TOC off --> | ||
=CGH: Appertures that are Parallel to the Image Screen= | =CGH: Appertures that are Parallel to the Image Screen= | ||
This chapter is intended primarily to replicate §I.A from the online class notes — see the original [http://www.phys.lsu.edu/faculty/tohline/phys4412/howto/ Table of Contents | This chapter is intended primarily to replicate [http://www.phys.lsu.edu/faculty/tohline/phys4412/howto/slit1d.html §I.A from the online class notes] — see also an associated [[User:Tohline/Appendix/CGH/Preface|Preface]] and the original [http://www.phys.lsu.edu/faculty/tohline/phys4412/howto/ Table of Contents] — that I developed in conjunction with a course that I taught in 1999 on the topic of ''Computer Generated Holography (CGH)'' for a subset of LSU physics majors who were interested in computational science. | ||
{{LSU_HBook_header}} | {{LSU_HBook_header}} | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
==One-Dimensional Aperture== | ==One-Dimensional Aperture== | ||
===General Concept=== | ===General Concept=== | ||
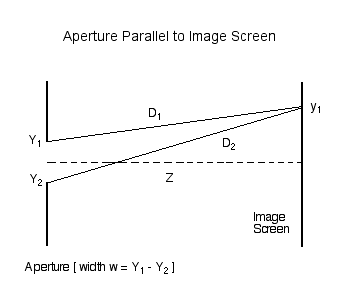
Consider the amplitude (and phase) of light that is incident at a location <math>~y_1</math> on an image screen that is located a distance <math>~Z</math> from a slit of width <math>~w</math>. | Consider the amplitude (and phase) of light that is incident at a location <math>~y_1</math> on an image screen that is located a distance <math>~Z</math> from a slit of width <math>~w</math>. First, as illustrated in Figure 1, consider the contribution due only to two rays of light: one coming from location <math>~Y_1</math> at the top edge of the slit (a distance <math>~D_1</math> from point <math>~y_1</math> on the screen) and another coming from location <math>~Y_2</math> at the bottom edge of the slit (a distance <math>~D_2</math> from the same point on the screen). | ||
<table border="1" cellpadding="5" align="center"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<th align="center">Figure 1</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td align="center" bgcolor="lightgreen">[[File:Aperture3.gif|Chapter1Fig1]]</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
=See Also= | =See Also= | ||
Revision as of 20:31, 9 November 2017
CGH: Appertures that are Parallel to the Image Screen
This chapter is intended primarily to replicate §I.A from the online class notes — see also an associated Preface and the original Table of Contents — that I developed in conjunction with a course that I taught in 1999 on the topic of Computer Generated Holography (CGH) for a subset of LSU physics majors who were interested in computational science.

|
|---|
| | Tiled Menu | Tables of Content | Banner Video | Tohline Home Page | |
One-Dimensional Aperture
General Concept
Consider the amplitude (and phase) of light that is incident at a location <math>~y_1</math> on an image screen that is located a distance <math>~Z</math> from a slit of width <math>~w</math>. First, as illustrated in Figure 1, consider the contribution due only to two rays of light: one coming from location <math>~Y_1</math> at the top edge of the slit (a distance <math>~D_1</math> from point <math>~y_1</math> on the screen) and another coming from location <math>~Y_2</math> at the bottom edge of the slit (a distance <math>~D_2</math> from the same point on the screen).
| Figure 1 |
|---|
 |
See Also
- Tohline, J. E., (2008) Computing in Science & Engineering, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 84-85 — Where is My Digital Holographic Display? [ PDF ]

|
|---|
|
© 2014 - 2021 by Joel E. Tohline |