Difference between revisions of "User:Tohline/ThreeDimensionalConfigurations/MeetsCOLLADAandOculusRiftS"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
{{LSU_HBook_header}} | {{LSU_HBook_header}} | ||
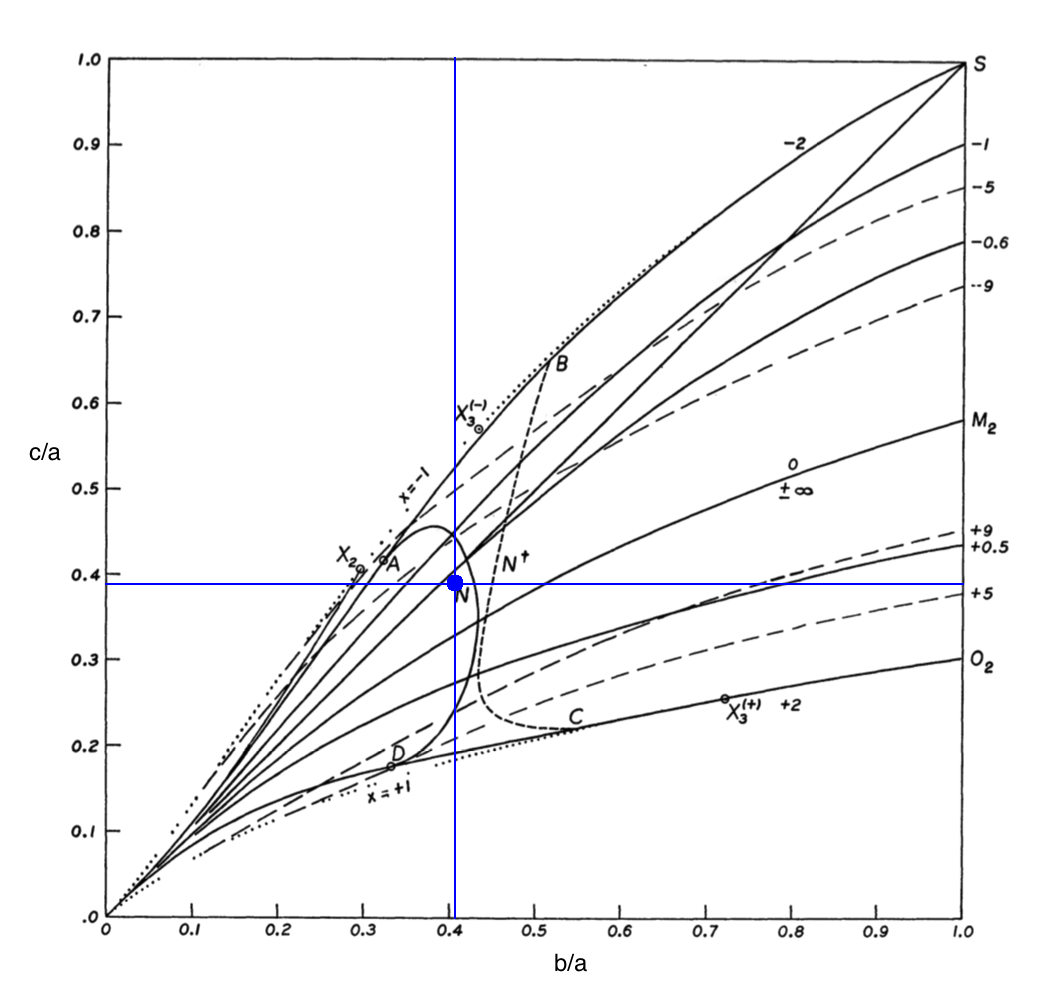
The EFE model that we have chosen to use in our first successful construction of a COLLADA-based, 3D and interactive animation has the following properties (model selected from [[User:Tohline/ThreeDimensionalConfigurations/RiemannStype#Table2|Table 2 of our accompanying discussion of Riemann S-type ellipsoids]]): | |||
<table border="0" cellpadding="5" align="center"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td align="right"> | |||
<math>~\frac{b}{a}</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> | |||
<math>~=</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="left"> | |||
<math>~0.41</math> | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td align="right"> | |||
<math>~\frac{c}{a}</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> | |||
<math>~=</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="left"> | |||
<math>~0.385</math> | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td align="right"> | |||
<math>~\Omega_\mathrm{EFE}</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> | |||
<math>~=</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="left"> | |||
<math>~ \frac{\omega}{\sqrt\pi } = \frac{0.971082}{\sqrt\pi} = 0.547874</math> | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td align="right"> | |||
<math>~\lambda_\mathrm{EFE}</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> | |||
<math>~=</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="left"> | |||
<math>~ \frac{0.141594}{\sqrt\pi} = 0.079886</math> | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
<div align="center"> | <div align="center"> | ||
| Line 16: | Line 69: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td align="left" bgcolor="white"> | <td align="left" bgcolor="white"> | ||
[[File:EFE_STypeRiemannDiagram04.png|300px|EFE Parameter Space]] | [[File:EFE_STypeRiemannDiagram04.png|300px|EFE Parameter Space]] | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
<td align="left" bgcolor="lightgrey"> | <td align="left" bgcolor="lightgrey"> | ||
[[File: | [[File:COLLADA1stViewpoint.png|300px|EFE Model b41c385]] | ||
</td> | |||
<td align="left" bgcolor="lightgrey"> | |||
[[File:COLLADA2ndViewpoint.png|250px|EFE Model b41c385]] | |||
</td> | </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 29: | Line 82: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
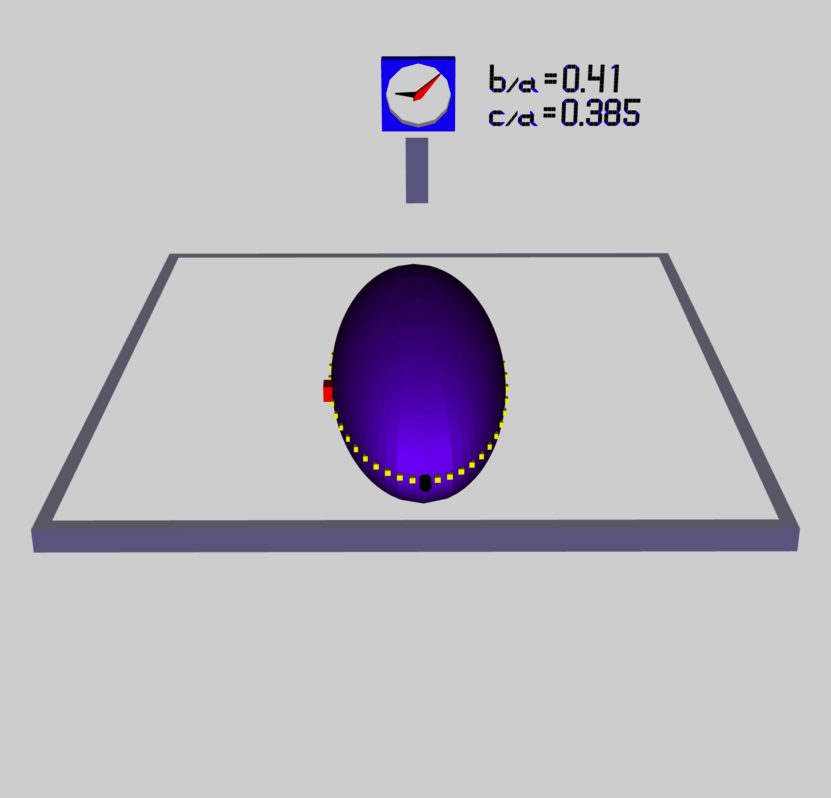
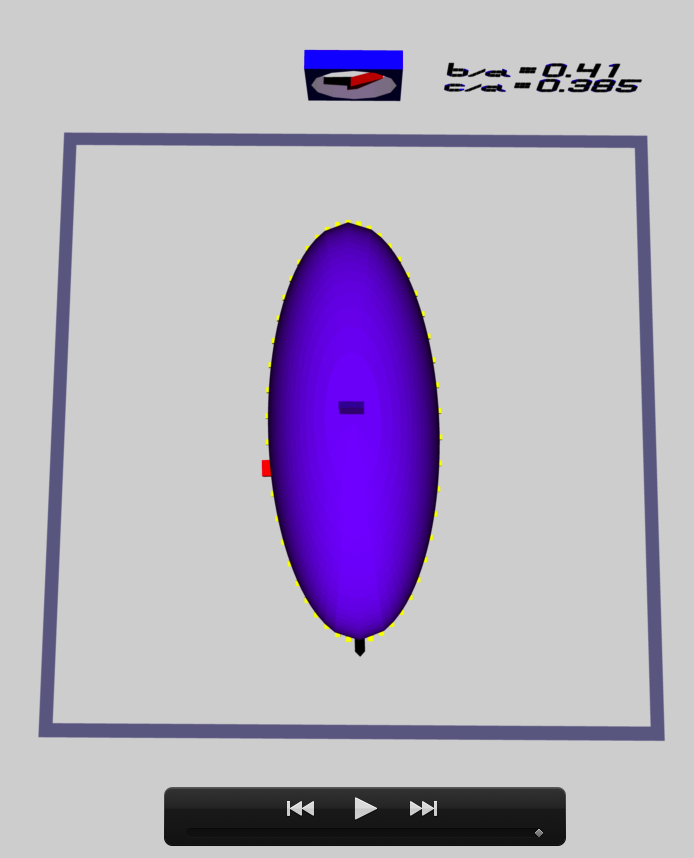
Figure 1 displays a pair of still-frame images of this (purple) ellipsoidal configuration after the ellipsoid has completed precisely five (counter-clockwise) spin cycles. (The snapshots have been taken at the same point in time, but from two different "camera" viewing angles.) The cycle of the "wall mounted" clock is based on the fundamental, EFE-adopted frequency of [π G ρ]<sup>½</sup>. In the left-hand image (labeled Figure 1a), the time on the clock appears to be about 9:08. This means that as the ellipsoid has completed five spin cycles, the clock has completed approximately [9 + 8/60] ≈ 9.13 cycles. In other words, the ratio (ellipsoid-to-clock) of these two frequencies is, | Figure 1 displays a pair of still-frame images of this (purple) ellipsoidal configuration after the ellipsoid has completed precisely five (counter-clockwise) spin cycles. (The snapshots have been taken at the same point in time, but from two different "camera" viewing angles.) The cycle of the "wall mounted" clock is based on the fundamental, EFE-adopted frequency of [π G ρ]<sup>½</sup>. In the left-hand image (labeled Figure 1a), the time on the clock appears to be about 9:08. This means that as the ellipsoid has completed five spin cycles, the clock has completed approximately [9 + 8/60] ≈ 9.13 cycles. In other words, the ratio (ellipsoid-to-clock) of these two frequencies is, | ||
Revision as of 23:59, 19 May 2020
Riemann Meets COLLADA & Oculus Rift S

|
|---|
| | Tiled Menu | Tables of Content | Banner Video | Tohline Home Page | |
The EFE model that we have chosen to use in our first successful construction of a COLLADA-based, 3D and interactive animation has the following properties (model selected from Table 2 of our accompanying discussion of Riemann S-type ellipsoids):
|
<math>~\frac{b}{a}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~0.41</math> |
|
<math>~\frac{c}{a}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~0.385</math> |
|
<math>~\Omega_\mathrm{EFE}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{\omega}{\sqrt\pi } = \frac{0.971082}{\sqrt\pi} = 0.547874</math> |
|
<math>~\lambda_\mathrm{EFE}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{0.141594}{\sqrt\pi} = 0.079886</math> |
Figure 1 displays a pair of still-frame images of this (purple) ellipsoidal configuration after the ellipsoid has completed precisely five (counter-clockwise) spin cycles. (The snapshots have been taken at the same point in time, but from two different "camera" viewing angles.) The cycle of the "wall mounted" clock is based on the fundamental, EFE-adopted frequency of [π G ρ]½. In the left-hand image (labeled Figure 1a), the time on the clock appears to be about 9:08. This means that as the ellipsoid has completed five spin cycles, the clock has completed approximately [9 + 8/60] ≈ 9.13 cycles. In other words, the ratio (ellipsoid-to-clock) of these two frequencies is,
|
<math>~\frac{\Omega_\mathrm{EFE}}{[\pi G \rho]^{1 / 2}}</math> |
<math>~\approx</math> |
<math>~\frac{5}{9.13} = 0.548 \, .</math> |
This matches the tabulated value of <math>~\Omega_\mathrm{EFE}</math> presented above. Now, let's examine the motion of an example Lagrangian fluid element, which has been marked in the 3D scene by a red "arrow" riding in the equatorial plane and along the surface of the (purple) ellipsoidal figure. At time zero, the fluid marker was placed at the end of the longest axis of the ellipsoid that was nearest the "wall clock"; then, as time progressed and the ellipsoidal figure turned counter-clockwise, the fluid marker moved clockwise and completed less than one full "orbit" in the same time that the ellipsoidal figure completed five full spin cycles. In the right-hand image (labeled Figure 1b), we can see that relative to the ellipsoidal figure, the fluid marker has moved through approximately three-quarters of its assigned elliptical "orbit"; let's say, 73% of one full cycle. This means that the ratio of the Lagrangian fluid element's orbital frequency to the frequency of the wall-clock is,
|
<math>~\frac{\lambda_\mathrm{EFE}}{[\pi G \rho]^{1 / 2}}</math> |
<math>~\approx</math> |
<math>~\frac{0.73}{9.13} = 0.080 \, .</math> |
This matches the tabulated value of <math>~\lambda_\mathrm{EFE}</math> presented above.
See Also
- Discussion of Ou's Riemann-Like Ellipsoids
- Virtual Reality and 3D Printing
- Success Importing Animated Scene into Oculus Rift S
- Carefully (Re)Build Riemann S-type Ellipsoids Inside Oculus Rift Environment

|
|---|
|
© 2014 - 2021 by Joel E. Tohline |